
30/07/2024
Abstract
Conducting environmental audit is considered an effective environmental management tool for production enterprises. In addition, environmental audit is also considered a reliable information channel, providing management agencies with information on the environmental management situation of enterprises. In Vietnam, although environmental audit has been conducted by a number of organizations and units, there is currently no general technical guidelines as a reference document. Therefore, in some cases, key contents of environmental audit are being integrated into financial audits or inspection and examination processes.
Article 74 of the Law on Environmental Protection (LEP) 2020 stipulates that environmental audit includes two main contents: (1) auditing the use of energy, chemicals, raw materials, and scraps imported from abroad as raw materials for production; (2) auditing the pollution control and waste management. Through studying the concepts, characteristics, classification of environmental audit as well as technical guidelines for conducting environmental audit of some countries, it is shown that the first content about auditing the use of energy, chemicals, raw materials, and scraps imported from abroad as raw materials for production is the same as waste audit; the second content about auditing the pollution control and waste management is similar to the compliance audit. Therefore, this article proposes to develop technical guidelines for conducting environmental audit in Vietnam for two contents: waste audit and compliance audit.
1. Introduction
In fact, countries or some international organizations, when developing technical guidelines for conducting environmental audit, only focus on one specific content such as waste audit or compliance audit. A number of popular technical guidelines that have been issued such as: Guidelines for conducting waste audit of UNIDO and UNEP; Guidelines for waste audit in pulp and paper industries of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); Guidelines for waste audit; Compliance Audit Handbook of Australia; Guidelines for Compliance Audit of Malaysia…
Summary shows that the main and important contents of those documents are instructions on processes and methodologies for conducting audit. Basically, the processes for conducting waste audit and compliance audit are according to the processes for conducting environmental audit including 03 specific stages: pre-audit, on-site audit and post-audit. For each specific content of waste audit or compliance audit, the steps in each stage will have different instructions.
The LEP 2020 stipulates that conducting environmental audit needs to include both waste audit and compliance audit.
2. Technical guidelines for conducting environmental audit in Vietnam
2.1. Procedure for environmental audit
Technical processes for conducting environmental audit for production, business and service establishments have 03 stages and 10 steps. Details are shown in Figure 1.
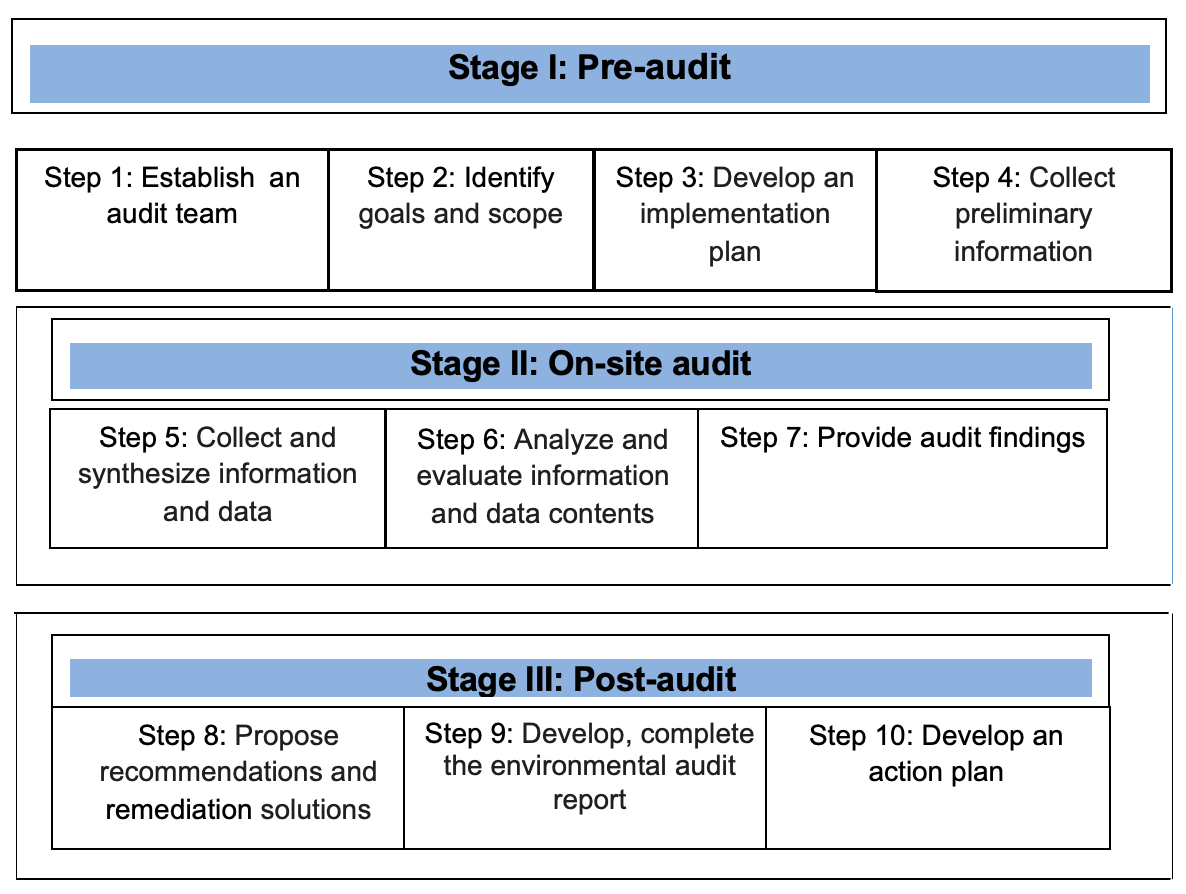
Figure 1: Detailed processes for self-conducting environmental audit at production, business and service establishments
With instructions on waste audit, the guidelines need to focus on instructions on implementing material balance, including instructions on collecting information and data, using materials, electricity, water and output information such as main products, by-products, types of waste... at factories and production facilities; instructions on calculating material balance of each production process or stage.
With instructions on compliance audit, the important content is to develop a checklist, including a set of questions to collect information related to environmental management, evaluate the compliance with legal regulations on environmental protection of establishments based on evaluation criteria.
2. Tools and techniques
Some tools that can be used in environmental audit at companies and enterprises:
• Checklist: A very useful tool used to ensure that various contents or topics are covered during the audit. A checklist is useful in specialized cases where a complex set of issues and questions need to be asked to ensure nothing is overlooked.
• Questionnaires: Evaluation protocols or evaluation questionnaires provide the basis and structure for most evaluations. They are based on checklist questionnaires but are more complex and include more details, sometimes logistical information and data related to the evaluation and the location being evaluated.
• Interview: A method of checking information through interviewing relevant individuals. Interview is an integral part of an audit. Interview answers can provide auditors with information that auditors did not previously have or provide corroborating audit evidence.
• Observation: An important component of an evaluation test.
• Images: A very valuable aid during the audit process. However, to use this method, several important practical points must be kept in mind, the most important of which is official approval before using this technique.
• Sampling: Various sampling techniques such as random sampling, stratified random sampling, judgmental sampling, purposive sampling, etc., can be used during the evaluation process.

Conducting environmental audit is considered an effective environmental management tool for production enterprises
Besides the general technical tools mentioned above, depending on each type of environmental audit, a number of specialized technical methods can be applied. Specifically, for this type of waste audit, the material balance method is also applied. Material balance is an important tool for identifying losses and verifying quantitative data of input materials and output waste of the production process. Material balance must be carried out individually for all raw materials used and products, waste generated from the production process. When there is a chemical reaction taking place in a system, it is convenient to perform "elemental balance" for the chemical elements in a system. Material balance can assist in identifying the concentrations of waste components generated.
2.3. Report templates for self-conducting environmental audit at production, business and service establishments
In addition to the main contents introducing general information about the audited establishment, audit objectives, plans and methods, it is necessary to present the results of environmental audit of the establishment. Contents to be presented are as follows:
a) Results of collecting and synthesizing information, data
- General presentation of input information, data serving production activities at the production and business establishment.
- General presentation of output information, data at the selected production and business establishment, including:
b) Analysis and evaluation of the results of environmental audit
- Results of material balance implementation
- Results of evaluation of compliance with regulations on pollution control and waste management
c) Audit findings
- Problems found in the efficiency of using input materials, sources of waste generation and origin of waste generation.
- Problems found in the compliance and non-compliance with pollution control and waste management regulations.
d) Proposed action plan
- Action plan to minimize loss and waste of input materials and reduce waste generation.
- Action plan to achieve better compliance with pollution control and waste management regulations.
3. Conclusion
This article proposes processes, methodologies and report templates to conduct environmental audit according to the contents specified in Article 74 of the LEP 2020. The guidelines when issued, will help production, business and service establishments research, learn and apply environmental audit themselves, thereby helping environmental auditing tools be more widely spread and popularized and become an effective internal environmental management tool.
MSc. Hàn Trần Việt, MSc. Trần Bích Hồng
Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment
(Source: The article was published on the Environment Magazine by English No. II/2024)
References
1. World Bank, 2016, Environmental Audit Report.
2. Office of the Auditor General of Nepal, Environmental Audit Guide.
3. Department of Environment Malaysia, (2011), Environmental Audit Guidance Manual.
4. ASOSAI, 2006, Guidance on Conducting Environmental Audit, 8th India, China, Malaysia, Pakistan and Saudi Arabia ASOSAI Research Project.
5. Internal Audit Standards Board (IASB), 2012, Guide on Environmental Audit.
6. The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, the Publication Department on behalf of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (2013) Technical Guide on Auditing Waste Management (2013).
7. Ajay Kumar et al (2017), Environment Audit in Electronics Industry Noida: A Case Study.
8. Shweta Gaur et al (2018), Environmental auditing as a risk management tool: case study of an automobile axle manufacturing industry in India.