
16/05/2018
In the past time, with the strong population growth and the formation and development of production sectors, the demand for commodities, raw materials, and energy, and the generation of solid waste have increased. In addition, the management and treatment of solid waste in our country has not focused on solutions to reduce, reuse, recycle and recover energy from waste, which results in environmental pollution. Therefore, strengthening the capacity for integrated municipal solid waste management is of great importance in improving the efficiency of solid waste management and improving environmental quality in Việt Nam.
According to the National State of Environment Report in 2016 - with the topic of "Urban environment" prepared by the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, the status of municipal solid waste generation and treatment in the urban area remains one of the emerging environmental issues over the past years. According to statistics, the generated domestic solid waste in the urban area is about 38,000 tons/day, with an average increase rate of 12%/year. Urban domestic solid waste has an organic proportion of about 54 - 77%, recyclable waste (plastic and metal components) is of about 8 - 18%. Generated medical solid waste is 600 tons/day with an increase rate of about 7.6%/year. Regarding industrial solid waste in the urban area, there is no specific statistics, but the volume is increasing, mainly from mechanical, textile, footwear and foodstuff industries. Estimated ratio of hazardous waste in industrial solid waste accounts for about 20 - 30%.
According to the report, the results of classification, collection and treatment of solid waste have been achieved to some extent. The average domestic solid waste collection and treatment proportion was about 85% in 2014 and increased up to 85.3% in 2015. The common domestic solid waste treatment technology is landfilling, composting and burning. In urban areas, domestic solid waste proportion for landfilling is approximately 34%, domestic solid waste proportion for recycling at treatment facilities is about 42% and the remaining landfilled solid waste is the residue of treatment processes, accounting for approximately 24%. The majority of municipal domestic solid waste is not separated at source. For medical solid waste, more than 90% of hospitals carried out collection and classification of waste at source, with a collection ratio of over 75% (2015). Beside achievements, the classification, collection and treatment of solid waste has some limitations such as high number of unhygienic landfills, lack of wastewater and emission collection and treatment system, resulting in environmental pollution. In particular, the habit of using plastic bags in our country has led to large amount of inorganic waste... By 2015, the country has about 35 solid waste treatment plants (not including about 50 incinerators with capacity of about 500 kg/hour), concentrated in urban areas, with an average capacity of 100 - 200 tons/day. Compared with 2012, the treated solid waste has increased by about 3,600 tons/day, but if compared to the current increase level of municipal solid waste, the solid waste treatment has not been as effective as expected.
In order to put in place integrated municipal solid waste management at a national level according to the National Strategy on Integrated Solid Waste Management, the Department of Technical Infrastructure (Ministry of Construction) and the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) in Việt Nam have cooperated to implement the project on "Strengthening the capacity of integrated municipal solid waste management in Việt Nam". The project was implemented from April 2014 to March 2018, with pilot activities in Hà Nội and Thừa Thiên - Huế province. The project has such components as institutional and management capacity strengthening, policy formulation on solid waste management; support to amend and perfect legal documents and technical standards on solid waste management; capacity strengthening of local authorities for solid waste management and technical assistance in developing the Master Plan in the Integrated Solid Waste Management…
After 4 years of implementation, the project has supported the Ministry of Construction to review the policies, regulations, institutional framework and standards for municipal solid waste management; to review and evaluate traditional and modern technologies in terms of treatment and management, and recommend appropriate technology selection criteria; to guide the planning on construction of municipal solid waste treatment facilities; to strengthen the capacity to inspect and supervise the management of municipal solid waste in localities; to collect data aiming at strengthening municipal solid waste management at the central level, to analyze and assess the existing problems. On the other hand, to study the investment and management models applicable to the construction of complexes for solid waste treatment; to study and guide the planning of construction of inter-provincial municipal solid waste treatment complexes; to organize training on strengthening municipal solid waste management in terms of institutional framework, management mechanism, technologies and responsibilities of stakeholders; to give comments on the draft of the revised National Strategy for Integrated Solid Waste Management to 2025 with a vision to 2050.
Along with that, the project has strengthened the capacity of the Hanoi Department of Construction in municipal solid waste management; evaluating the results of the project (Phase 1) from a sustainability perspective of the activities and analyzing the current status of the city's solid waste management system; identifying lessons learned and making recommendations; consulting on implementation of Master Plan (M/P) on Solid Waste Management of Hà Nội; technically consulting on the selection of solid waste treatment areas under the M/P on Solid Waste Management of Hà Nội and conducting pre-feasibility studies for selected solid waste treatment areas; studying and attracting investment in the construction of solid waste treatment areas... The project has also supported Thừa Thiên - Huế province to complete the data aggregation and develop the Province’s M/P on Integrated Solid Waste Management. The M/P includes detailed and specific calculation of waste volume generated per capita based on the data of the provincial weighing station; forecasting the amount of waste generated in the coming years. In particular, Thừa Thiên - Huế has conducted planning of 3 waste collection areas in the province; calculating transport modes, waste treatment technologies and financial resources as well as related institutions and policies to implement the planning.
In addition, the project has completed 6 guiding documents including: Preparation of M/P on integrated solid waste management, focusing on domestic solid waste; Preparation of medium-term and long-term development plans for solid waste treatment facilities; Selection of appropriate technologies for domestic solid waste treatment; Planning on the construction of solid waste treatment facilities; Investment in constructing and managing the operation of domestic solid waste treatment facilities; and Sustainable financial system for solid waste management. The project has also disseminated the products and delivered the results to the localities throughout the country.
In general, the activities of the project have had a profound impact on localities through the collection of solid waste management data, technical seminars, training programs in Japan and in the country, experience sharing… contributing to raising awareness and responsibility in environmental protection by managers, enterprises operating in the field of environment and the community.
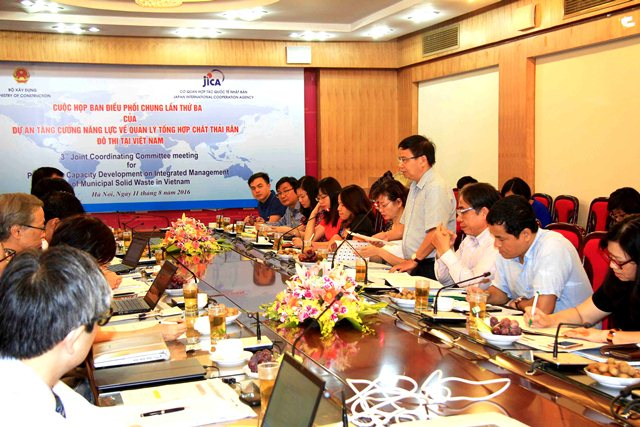

The 3rd Joint Coordination Committee Meeting of the Project "Strengthening the capacity of integrated municipal solid waste management in Việt Nam" was held in August 2016.
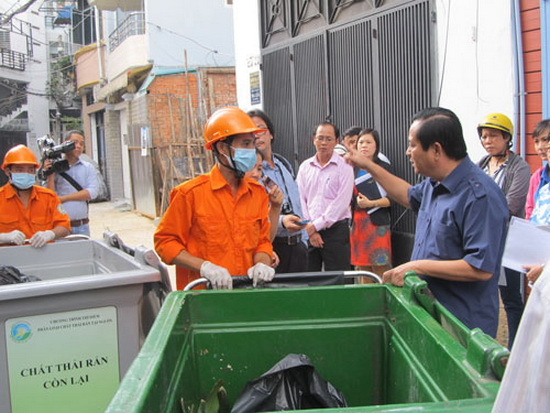

Waste separation at source - an important step in the treatment of municipal solid waste
Lê Văn Kha
Ministry of Construction
(Source: Vietnam Environment Administration Magazine, English Edition I-2018)