
03/01/2025
High integrity carbon credit markets can play an important role in accelerating global decarbonization toward net-zero emissions. To achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 and keep a limit of 1.5°C temperature rise within reach, it is crucial to accelerate action by 2030, increase ambition and urgently implement current nationally determined contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement and the collective long-term global aspirational goal adopted by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Member States.
Enhance the integrity of voluntary carbon credit markets
These ambitious goals can be advanced by, among other actions, supporting greenhouse gas mitigation actions that generate high integrity carbon credits. In order to achieve this, they need to be consistent with a pathway toward overall net-zero emissions; in particular, both creation and use of credits need to be supplementary to immediate efforts to reduce emissions in line with science-aligned pathways, and should avoid lock-in of high emissions pathways and contribute to the implementation of host country targets such as by sharing mitigation benefits.
Source: climateactionreserve.org
In addition to mobilizing climate finance from public and private sources, high integrity carbon credit markets can, where necessary safeguards are in place, provide sufficient demand to promote deployment of clean, safe and sustainable decarbonizing technologies and investment in nature-based solutions, unlocking social and environmental co-benefits.
There is a growing need to enhance the integrity of voluntary carbon credit markets and their alignment to the goals of the Paris Agreement, including their incorporation of best practices related to carbon crediting mechanisms. This set of “Principles of High Integrity Carbon Markets” can inform global efforts to enhance integrity of carbon credits to allow all stakeholders to take advantage of the full potential of carbon markets for both voluntary and compliance purposes.
These include relevant rules, guidance, and procedures developed multilaterally under Article 6 of the Paris Agreement and for ICAO’s Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA) and through independent multistakeholder initiatives. We will strive to promote these principles where appropriate in the development of carbon credit markets. We also emphasize that these principles are non exhaustive and require robust interpretation and implementation, and refinement as necessary, to ensure that they reinforce science and best practices for aligning carbon markets with ambitious global emissions pathways.
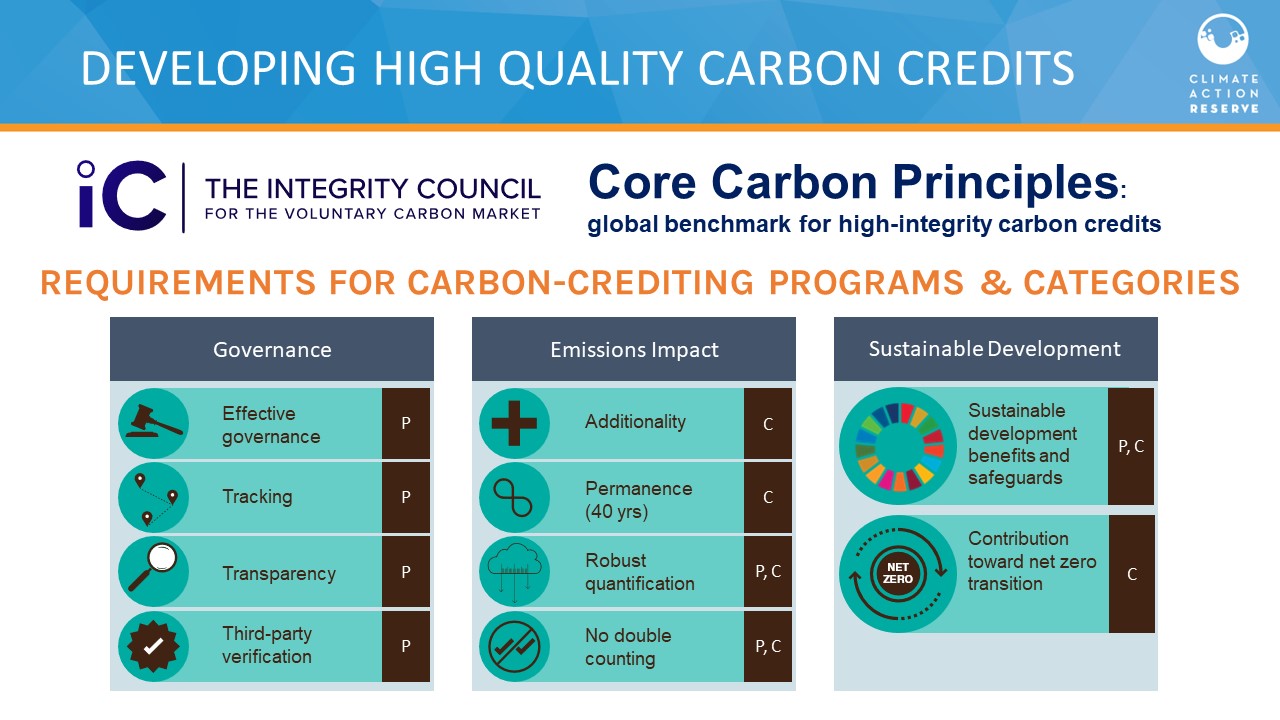
The principles for high integrity carbon credit markets
The following principles for high integrity carbon credit markets apply to strategies and standards guiding their supply, demand, and market infrastructure to improve credibility, transparency, and overall confidence in the markets.
Source: climateactionreserve.org
Supply-side Integrity: A robust certification standard is applied to activity design and measurement, reporting, and verification (MRV) of emission reductions or removals, with procedures that ensure the following aspects of the supported activities and resulting greenhouse gas mitigation: Crediting levels align with emissions pathways consistent with the Paris Agreement temperature goal and achievement of global net-zero emissions by 2050; Credits are issued for emission reductions or removals that clearly contribute to host country mitigation, and avoid lock-in of high emissions pathways, and where climate change mitigation strategies are in place that prioritize direct mitigation action; Alignment with relevant requirements for ensuring environment integrity and the CORSIA emissions units criteria and guidelines, including in reporting requirements under guidance on cooperative approaches and elements reflecting emerging best practices, in particular for ambitious baseline-setting, additionality assessment, avoidance of emissions lock in, emissions leakage accounting, permanence, and the avoidance of all forms of double-counting; Robust and transparent governance, with procedures in place to ensure transparency and, public accountability including with respect to decisions and decision-making processes, as well as the long-term administration of the standard issued credits and their ownership; Sustainable development objectives and resulting benefits are transparently reported. Environmental and social impacts are identified, publicly disclosed, and addressed through safeguards including monitoring. Human rights, gender equality and the rights of indigenous people are respected.
Demand-side Integrity: The use of credits, included by the private sector, align with keeping a limit of 1.5°C temperature rise within reach and achievement of global net-zero emissions by 2050, in relation to unavoidable emissions and where science-based climate change mitigation strategies and targets are in place that prioritize direct action to mitigate emissions. Emission reductions or removals underpinning carbon credits are claimed for use to achieve NDCs and other international mitigation purposes only when they are authorized according to the Guidance on cooperative approaches and eligible for such use. The use of carbon credits is disclosed through reporting processes that make such information transparent to and easily accessible by the public, to allow for public accountability and encourage investments in mitigation actions such as beyond the value chain. This includes information on the types, sources, and quantities of credits used.
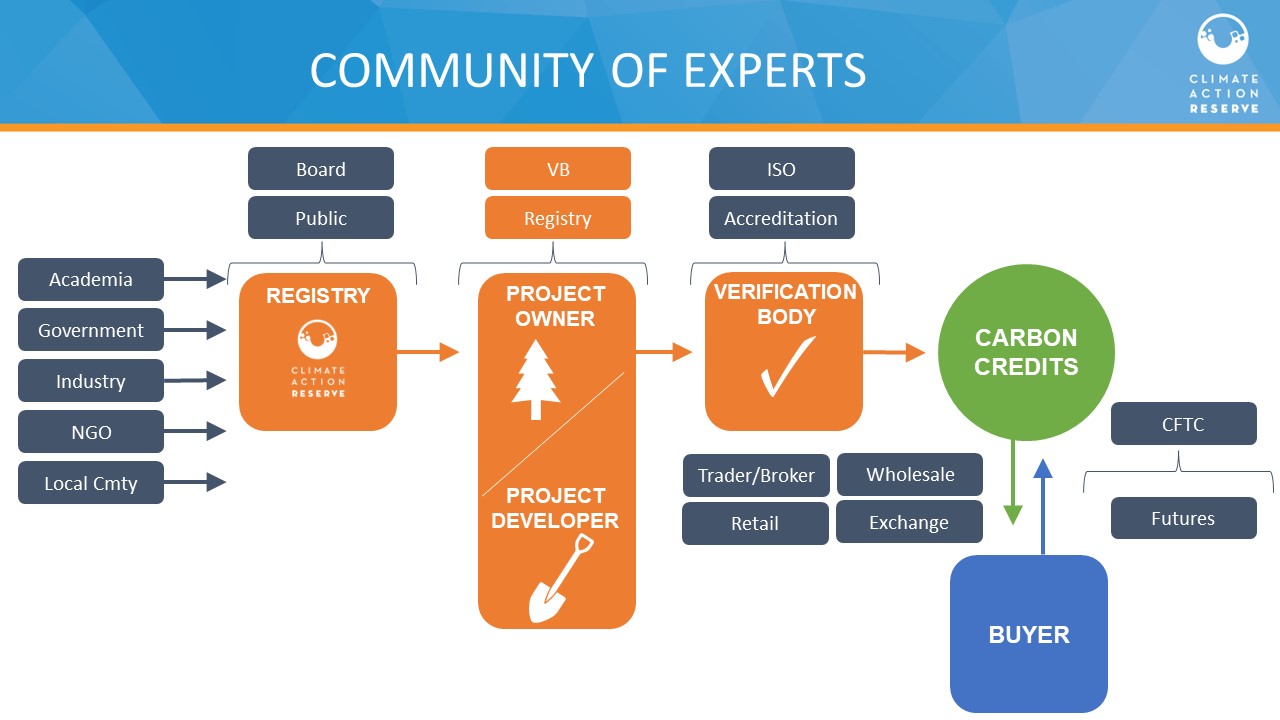
Market Integrity Registries publicly track information necessary for compliance and voluntary carbon credit market integrity, including enabling users and the public to identify market eligibility, the status of authorization and corresponding adjustments, and the purpose of use. Emissions across all scopes and associated targets, and strategies and annual progress toward their implementation, are transparently disclosed and tracked, including any use of carbon credits as well as any targeted investments in beyond value-chain mitigation, to enhance integrity and appropriate signaling between supply and demand-side participants in the carbon credit markets. Global standard-setting bodies and initiatives cooperate to align standards, clarify their respective services or roles, and continually innovate certification products that will meet and exceed current practice and expectations of regulators and other stakeholders to reduce carbon credit market fragmentation and promote a uniform shift to high integrity.
Nhâm Hiền
(Source: The G7 Ministers' Meeting on Climate, Energy and Environment in Sapporo)
(Source: The article was published on the Environment Magazine by English No. IV/2024)